codeforces-757-【B、C思维】
来源:互联网 发布:怎么样信任软件 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/11 18:19
题目链接:点击打开链接
Bash wants to become a Pokemon master one day. Although he liked a lot of Pokemon, he has always been fascinated by Bulbasaur the most. Soon, things started getting serious and his fascination turned into an obsession. Since he is too young to go out and catch Bulbasaur, he came up with his own way of catching a Bulbasaur.
Each day, he takes the front page of the newspaper. He cuts out the letters one at a time, from anywhere on the front page of the newspaper to form the word "Bulbasaur" (without quotes) and sticks it on his wall. Bash is very particular about case — the first letter of "Bulbasaur" must be upper case and the rest must be lower case. By doing this he thinks he has caught one Bulbasaur. He then repeats this step on the left over part of the newspaper. He keeps doing this until it is not possible to form the word "Bulbasaur" from the newspaper.
Given the text on the front page of the newspaper, can you tell how many Bulbasaurs he will catch today?
Note: uppercase and lowercase letters are considered different.
Input contains a single line containing a string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 105) — the text on the front page of the newspaper without spaces and punctuation marks. |s| is the length of the string s.
The string s contains lowercase and uppercase English letters, i.e.  .
.
Output a single integer, the answer to the problem.
Bulbbasaur
1
F
0
aBddulbasaurrgndgbualdBdsagaurrgndbb
2
In the first case, you could pick: Bulbbasaur.
In the second case, there is no way to pick even a single Bulbasaur.
In the third case, you can rearrange the string to BulbasaurBulbasauraddrgndgddgargndbb to get two words "Bulbasaur".
#include<cstdio>#include<cstring>#include<algorithm>using namespace std;char str[100010];int num[20];int main(){while(~scanf("%s",str)){memset(num,0,sizeof(num));int len=strlen(str);if(len<9){puts("0");continue;}for(int i=0;i<len;i++){if(str[i]=='B')num[1]++;if(str[i]=='u')num[2]++;if(str[i]=='l')num[3]++;if(str[i]=='b')num[4]++;if(str[i]=='a')num[5]++;if(str[i]=='s')num[6]++;if(str[i]=='r')num[7]++;}num[2]>>=1; num[5]>>=1;int ans=100010;for(int i=1;i<=7;i++)ans=min(ans,num[i]);printf("%d\n",ans);}return 0;}题目链接:点击打开链接
#include<cstdio>#include<algorithm>#include<cstring>using namespace std;int n;int vis[100010];int main(){while(~scanf("%d",&n)){memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));while(n--){int x;scanf("%d",&x);vis[x]++;}int ans=1;for(int i=2;i<=100000;i++){int tp=0;for(int j=i;j<=100000;j+=i){tp+=vis[j];}ans=max(ans,tp);}printf("%d\n",ans);}return 0;}题目链接:点击打开链接
It's that time of the year, Felicity is around the corner and you can see people celebrating all around the Himalayan region. The Himalayan region has n gyms. The i-th gym has gi Pokemon in it. There are m distinct Pokemon types in the Himalayan region numbered from 1 to m. There is a special evolution camp set up in the fest which claims to evolve any Pokemon. The type of a Pokemon could change after evolving, subject to the constraint that if two Pokemon have the same type before evolving, they will have the same type after evolving. Also, if two Pokemon have different types before evolving, they will have different types after evolving. It is also possible that a Pokemon has the same type before and after evolving.
Formally, an evolution plan is a permutation f of {1, 2, ..., m}, such that f(x) = y means that a Pokemon of type x evolves into a Pokemon of type y.
The gym leaders are intrigued by the special evolution camp and all of them plan to evolve their Pokemons. The protocol of the mountain states that in each gym, for every type of Pokemon, the number of Pokemon of that type before evolving any Pokemon should be equal the number of Pokemon of that type after evolving all the Pokemons according to the evolution plan. They now want to find out how many distinct evolution plans exist which satisfy the protocol.
Two evolution plans f1 and f2 are distinct, if they have at least one Pokemon type evolving into a different Pokemon type in the two plans, i. e. there exists an i such that f1(i) ≠ f2(i).
Your task is to find how many distinct evolution plans are possible such that if all Pokemon in all the gyms are evolved, the number of Pokemon of each type in each of the gyms remains the same. As the answer can be large, output it modulo 109 + 7.
The first line contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n ≤ 105, 1 ≤ m ≤ 106) — the number of gyms and the number of Pokemon types.
The next n lines contain the description of Pokemons in the gyms. The i-th of these lines begins with the integer gi (1 ≤ gi ≤ 105) — the number of Pokemon in the i-th gym. After that gi integers follow, denoting types of the Pokemons in the i-th gym. Each of these integers is between 1 and m.
The total number of Pokemons (the sum of all gi) does not exceed 5·105.
Output the number of valid evolution plans modulo 109 + 7.
2 32 1 22 2 3
1
1 33 1 2 3
6
2 42 1 23 2 3 4
2
2 23 2 2 12 1 2
1
3 72 1 22 3 43 5 6 7
24
In the first case, the only possible evolution plan is:

In the second case, any permutation of (1, 2, 3) is valid.
In the third case, there are two possible plans:

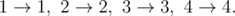
In the fourth case, the only possible evolution plan is:
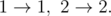
大意:给出 n 组数,每组 gi 个数,每个数属于1~m。每个数可以变化(若规定某一 gi 中的某一数 a 变为 b,那么剩余所有的 gi 中的 a 也变为 b),但变化前相同的数变化后依然相同(即 gi 里边元素的排列顺序发生了变化,元素的种类不变,同一种元素的个数不变),变化前不同的数变化后依然不同,且可能不变。但经过变化后每组的每种数的个数不会变化,求变化的总方案数。
思路:只有在每个 gym 上出现次数都相同的数 x,y 可以存在 f [x] = y 或 f [y] = x。那么最终在每个 gym 出现次数都相同的数会成为一个个集合。设这些集合的大小为 x1,x2,x3 ..... 显然对于一个大小为 x 的集合,方案数为 x!,即为他们的全排列数。那么 ans = x1! * x2! * x3! ..... xk!
#include<cstdio>#include<algorithm>#include<cstring>#include<vector>#include<map>#define LL long longusing namespace std;const LL MOD=1e9+7;int n,m;vector<int> G[1000010];map< vector<int>,int > M;map< vector<int>,int > ::iterator it;LL solve(int x){LL ans=1;for(int i=2;i<=x;i++){ans=ans*i%MOD;}return ans;}int main(){while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){for(int i=0;i<1000010;i++)G[i].clear();M.clear();for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){int x;scanf("%d",&x);while(x--){int y;scanf("%d",&y);G[y].push_back(i);}}for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)M[G[i]]++;LL cnt=1,ans=1;for(it=M.begin();it!=M.end();it++){ans=ans*solve(it->second)%MOD;}printf("%I64d\n",ans);}return 0;}/**************#include<cstdio>#include<algorithm>#include<cstring>#include<vector>#include<iostream>#define LL long longusing namespace std;const LL MOD=1e9+7;int n,m;vector<int> G[1000010];int main(){while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){for(int i=0;i<1000010;i++)G[i].clear();for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){int x;scanf("%d",&x);while(x--){int y;scanf("%d",&y);G[y].push_back(i);}}sort(G+1,G+m+1); // 之前压入的都是有序的,这里只排一级地址 LL cnt=1,ans=1;for(int i=2;i<=m;i++){if(G[i]==G[i-1]){cnt++;ans=ans*cnt%MOD;}elsecnt=1;}printf("%I64d\n",ans);}return 0;}**************/- codeforces-757-【B、C思维】
- codeforces-758【B、C思维】
- codeforces-500【B思维】【C贪心】
- codeforces-141【B找规律】【C思维】
- codeforces-743【B找规律】C思维】
- Codeforces-868B ,C 模拟,思维。。
- [思维]CodeForces 135B
- 【codeforces B + 思维】
- codeforces-233【B思维】
- CodeForces 219B (思维)
- Codeforces Round #447 (Div. 2) B C 思维
- Codeforces-298B 思维训练
- [思维]CodeForces 156B Suspects
- codeforces 361B 思维题
- CodeForces - 417B (思维题)
- Codeforces 599B-----思维题
- Codeforces 664 B Rebus【思维】
- Codeforces 115 B Lawnmower【思维】
- 查看Android应用包名的全部方法
- javascript 基础 图片库的动态速度与元素生成 2017年1月15日
- Uva712 S-Trees 【二分思想】【习题6-2】
- 问题五十七:怎么用ray tracing画translational sweeping图形
- What is LineageOS ? Everything you need to know about Lineage OS
- codeforces-757-【B、C思维】
- Ansible操作windows主机出现SL3_GET_SERVER_CERTIFICATE:certificate verify failed错误
- 堆内存设置、原理
- caffe.proto 注释理解
- 【LeetCode】 341. Flatten Nested List Iterator
- 浅谈Java中hashCode方法
- 程序优化_数据查询
- CSDN--我的收藏地址
- Jni中执行ndk-build,编译第三方静态库(.a)和动态库(.so)的Android.mk文件写法


