Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2)
来源:互联网 发布:网络咨询医生技巧例子 编辑:程序博客网 时间:2024/06/11 21:06
A. Soldier and Bananas
A soldier wants to buy w bananas in the shop. He has to pay k dollars for the first banana, 2k dollars for the second one and so on (in other words, he has to pay i·k dollars for the i-th banana).
He has n dollars. How many dollars does he have to borrow from his friend soldier to buy w bananas?
Input
The first line contains three positive integers k, n, w (1 ≤ k, w ≤ 1000, 0 ≤ n ≤ 109), the cost of the first banana, initial number of dollars the soldier has and number of bananas he wants.
Output
Output one integer — the amount of dollars that the soldier must borrow from his friend. If he doesn’t have to borrow money, output 0.
Sample test(s)
input
3 17 4
output
13
- 加减乘除…,注意不需要借钱的情况
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>int main(){ int n, k, w; while(~scanf("%d%d%d",&k,&n,&w)) { __int64 tmp = 0; if(w % 2 == 0) { tmp = (1 + w)*w/2; } else { tmp = (1 + w)*(w /2); tmp += (w/2) + 1; } printf("%I64d\n",tmp*k - n > 0 ? tmp*k - n : 0); }} B. Soldier and Badges
Colonel has n badges. He wants to give one badge to every of his n soldiers. Each badge has a coolness factor, which shows how much it’s owner reached. Coolness factor can be increased by one for the cost of one coin.
For every pair of soldiers one of them should get a badge with strictly higher factor than the second one. Exact values of their factors aren’t important, they just need to have distinct factors.
Colonel knows, which soldier is supposed to get which badge initially, but there is a problem. Some of badges may have the same factor of coolness. Help him and calculate how much money has to be paid for making all badges have different factors of coolness.
Input
First line of input consists of one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 3000).
Next line consists of n integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ n), which stand for coolness factor of each badge.
Output
Output single integer — minimum amount of coins the colonel has to pay.
Sample test(s)
input
4
1 3 1 4
output
1
input
5
1 2 3 2 5
output
2
Note
In first sample test we can increase factor of first badge by 1.
In second sample test we can increase factors of the second and the third badge by 1.
- 题意就是,让每个数都变成唯一的一个,所以就是依次加到离它最近的,还没出现过的那个数就可以了。
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;bool vis[6010];int tt[3010];int main(){ int n; while(~scanf("%d",&n)) { int sum = 0; memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis)); for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) { scanf("%d",&tt[i]); //vis[tt[i]] = true; } sort(tt, tt + n); for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) { if(!vis[tt[i]]) vis[tt[i]] = true; else { for(int j = tt[i]; ; j ++) { if(!vis[j]) { vis[j] = true; sum += (j - tt[i]); break; } } } } printf("%d\n",sum); } return 0;} C. Soldier and Cards
time limit per test2 seconds
memory limit per test256 megabytes
Two bored soldiers are playing card war. Their card deck consists of exactly n cards, numbered from 1 to n, all values are different. They divide cards between them in some manner, it’s possible that they have different number of cards. Then they play a “war”-like card game.
The rules are following. On each turn a fight happens. Each of them picks card from the top of his stack and puts on the table. The one whose card value is bigger wins this fight and takes both cards from the table to the bottom of his stack. More precisely, he first takes his opponent’s card and puts to the bottom of his stack, and then he puts his card to the bottom of his stack. If after some turn one of the player’s stack becomes empty, he loses and the other one wins.
You have to calculate how many fights will happen and who will win the game, or state that game won’t end.
Input
First line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 10), the number of cards.
Second line contains integer k1 (1 ≤ k1 ≤ n - 1), the number of the first soldier’s cards. Then follow k1 integers that are the values on the first soldier’s cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
Third line contains integer k2 (k1 + k2 = n), the number of the second soldier’s cards. Then follow k2 integers that are the values on the second soldier’s cards, from top to bottom of his stack.
All card values are different.
Output
If somebody wins in this game, print 2 integers where the first one stands for the number of fights before end of game and the second one is 1 or 2 showing which player has won.
If the game won’t end and will continue forever output - 1.
Sample test(s)
input
4
2 1 3
2 4 2
output
6 2
input
3
1 2
2 1 3
output
-1
Note
First sample:
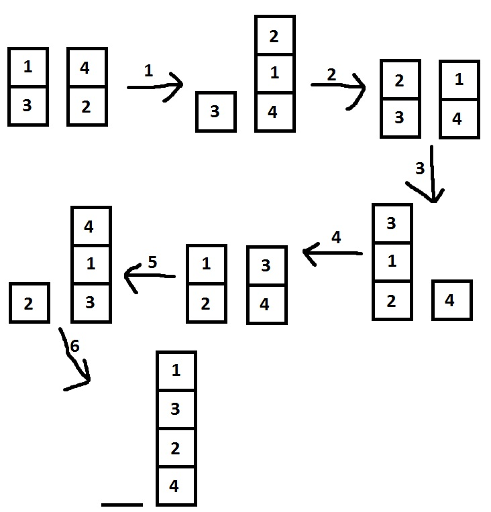
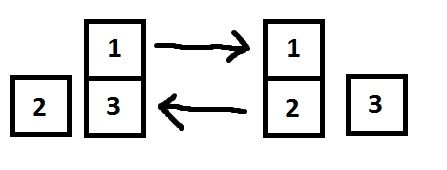
Second sample:
- 模拟+暴力
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <algorithm>#include <queue>#include <vector>using namespace std;int tt[11];int a, b;int main(){ int n; while(~scanf("%d",&n)) { queue<int> aa; queue<int> bb; while(!aa.empty()) { aa.pop(); } while(!bb.empty()) { bb.pop(); } scanf("%d",&a); for(int i = 0; i < a; i ++) { scanf("%d",&tt[i]); aa.push(tt[i]); } scanf("%d",&b); for(int i = a; i < n; i ++) { scanf("%d",&tt[i]); bb.push(tt[i]); } int cnt = 0; while(1) { if(aa.empty() || bb.empty()) break; int tmp_a = aa.front(); int tmp_b = bb.front(); aa.pop(); bb.pop(); if(tmp_a > tmp_b) { aa.push(tmp_b); aa.push(tmp_a); } else { bb.push(tmp_a); bb.push(tmp_b); } cnt ++; if(cnt > 1e6) { cnt = -1; break; } } printf("%d",cnt); if(cnt != -1) { printf(" %d",aa.empty() ? 2 : 1); } printf("\n"); } return 0;}D. Soldier and Number Game
time limit per test3 seconds
memory limit per test256 megabytes
Two soldiers are playing a game. At the beginning first of them chooses a positive integer n and gives it to the second soldier. Then the second one tries to make maximum possible number of rounds. Each round consists of choosing a positive integer x > 1, such that n is divisible by x and replacing n with n / x. When n becomes equal to 1 and there is no more possible valid moves the game is over and the score of the second soldier is equal to the number of rounds he performed.
To make the game more interesting, first soldier chooses n of form a! / b! for some positive integer a and b (a ≥ b). Here by k! we denote the factorial of k that is defined as a product of all positive integers not large than k.
What is the maximum possible score of the second soldier?
Input
First line of input consists of single integer t (1 ≤ t ≤ 1 000 000) denoting number of games soldiers play.
Then follow t lines, each contains pair of integers a and b (1 ≤ b ≤ a ≤ 5 000 000) defining the value of n for a game.
Output
For each game output a maximum score that the second soldier can get.
Sample test(s)
input
2
3 1
6 3
output
2
5
- the score of the second soldier is equal to the number of rounds he performed,理解一下这句。然后就是统计质因数的个数,在筛素数过程中实现
#include <stdio.h>#include <string.h>#include <algorithm>#include <queue>#include <vector>using namespace std;#define N 5000010int prime[N/10];bool is_prime[N];int ans[N]; void sieve(int n){ int p = 0; for(int i = 0; i <= n; i ++) { is_prime[i] = true; } is_prime[0] = is_prime[1] = false; for(int i = 2; i <= n; i ++) { if(is_prime[i]) { prime[p ++] = i; for(int j = i; j <= n; j += i) { int tmp = j; while(tmp % i == 0) { ans[j] ++; tmp/= i; } is_prime[j] = false; } } } for(int i = 2; i < N; i ++) { ans[i] = ans[i] + ans[i - 1]; }}int main(){ int t; int a, b; sieve(N); while(~scanf("%d",&t)) { while(t --) { scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); printf("%d\n", ans[a] - ans[b]); } } return 0;}- Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2) B
- Codeforces-B.Soldier and Badges - Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #102 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #103 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #103 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #104 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #105 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #105 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #107 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #108 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #110 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #122 (Div. 2)
- Codeforces Round #121 (Div. 2)
- 最新CocoaPods的安装及使用(持续更新中)
- JAVA多线程面试
- addevent()实现跨浏览器绑定事件
- 黑马程序员 JAVA基础学习日记五——封装 继承 多态
- 让UIScrollView只有一边有弹簧效果
- Codeforces Round #304 (Div. 2)
- leetcode H-Index
- $GLOBALS['HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA'] 和$_POST的区别
- mysqladmin创建MySQL数据库
- shader中的属性
- ac自动机模板-kuangbin
- GCD深入理解
- 泰森多边形(Voronoi图)生成算法
- B树、B-树、B+树、B*树都是什么


